Integrated request tests
RestApia supports request-based tests, allowing you to define and execute validations directly within request code. These tests help ensure API responses meet expectations by validating status codes, response times, content lengths, and JSON properties.
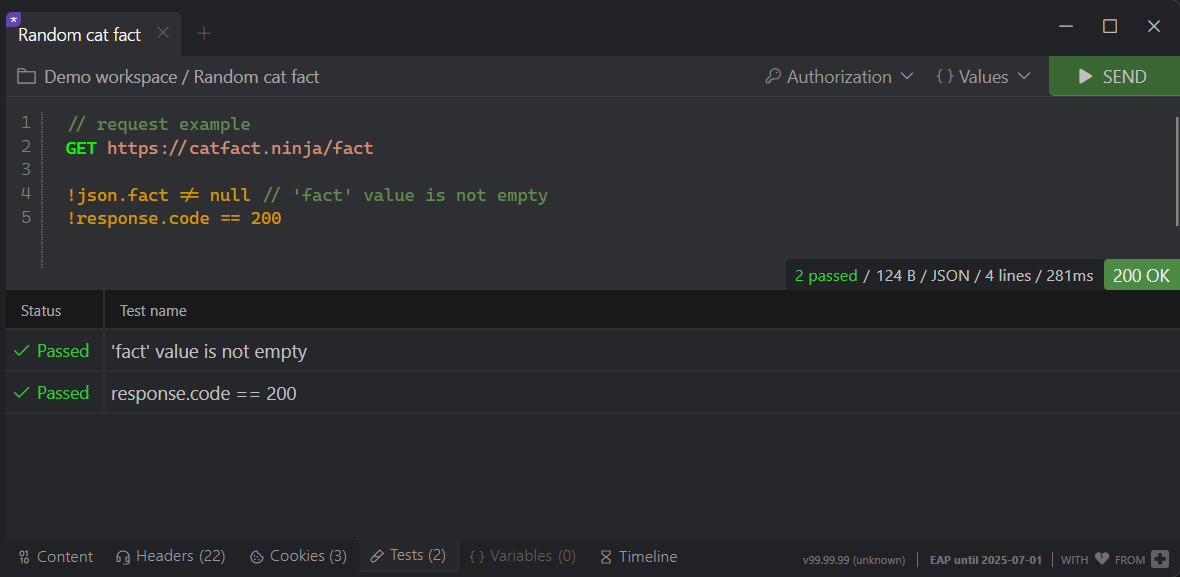
Writing Tests
Tests are written inline in request definitions using the ! prefix. They are evaluated as JavaScript expressions.
Example Test Usage
!response.code == 200
!json.id == "abc"
!response.time.milliseconds < 500 // expect Fast response
!response.length.kb > 3 // expect Sufficient payload size
!content.includes('fact') // response contains 'fact'
!headers['Content-Type'].includes('json') // response header contains 'json'
!cookies['catfacts_session'] != null // cookie 'catfacts_session' is set
Available Test Properties
Test commands in RestApia allow you to validate different aspects of API responses, including status codes, response times, and content lengths. These commands help ensure your API functions correctly by defining expectations within your request code.
HTTP Status Code
response.code→ HTTP status code of the response.
Response Time
response.time.milliseconds→ Total response time in milliseconds.response.time.seconds→ Total response time in seconds.response.time.minutes→ Total response time in minutes.
Response Content Length
response.length.bytes→ Response size in bytes.response.length.kb→ Response size in kilobytes.response.length.mb→ Response size in megabytes.
More objects for Testing
content→ Response content as a Stringheaders→ Dictionary of Response Headerscookies→ Dictionary of Cookies
JSON Response Handling
If the response contains JSON, the json object is automatically available for property validation.
!json.name == "admin" // valid user role
!json.roles.contains("editor") // roles array contains "editor"
More testing functions
log('your message here or object')→ Logs a message or object as test output.
Custom Test Naming
By default, test results display the original validation expression. You can provide custom test names using comments in the same line with test // expect <description>.
!response.code == 200 // expect OK HTTP code
!response.time.milliseconds < 500 // expect Fast response
These descriptions appear in the Tests tab alongside pass/fail statuses.
Future Improvements
The test feature will be expanded with additional functionality. Future updates will introduce support for building test cases and test sequences to enhance test automation and workflow flexibility.
